There is always a risk of a fammable hydrocarbon release in the oil and gas industry. When the release comes into contact with air and an ignition source, an explosion can happen. Oil & gas and chemical industries generated many accidents (fire ,explosion).
In a situation in which there may be an explosive (flammable) atmosphere , the
following steps should be taken:
a) eliminate the likelihood of an explosive gas atmosphere occurring around the source of ignition, or b) eliminate the source of ignition.
Where this is not possible, protective measures, process equipment, systems and procedures should be selected and prepared so the likelihood of the coincidence of a) and b) is so small as to be acceptable.
Where this is not possible, protective measures, process equipment, systems and procedures should be selected and prepared so the likelihood of the coincidence of a) and b) is so small as to be acceptable.
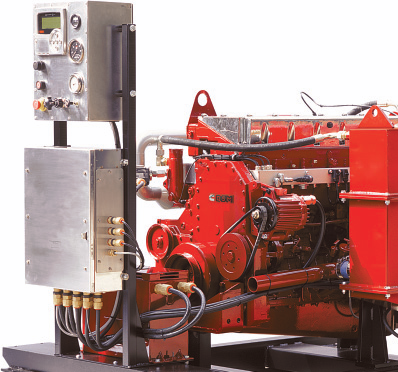
Zone 2 diesel engine and zone 2 diesel generators are designed to reduce the risk of an engine being the source of ignition.
Potential ignition sources on unprotected diesel engines include electrical, mechanical or static sparks, overspeed or ame transmission from inlet or exhaust, and hot surfaces.
Flammable gases in the atmosphere can be drawn in through the air intake along with air for combustion. This can result in ashbacks through the inlet and back res in the exhaust.
If the engine consumes ammable gas mixed with air and diesel fuel, engine overspeed can occur, which can lead to the engine running out of control. This can result in catastrophic failure of the engine, creating unprotected ignition sources.
Another risk is engine mis ring, leading to unburnt fuel mixture entering the exhaust system. This can be detonated from the heat of the exhaust and ignite the surrounding atmosphere.
Various surfaces on a diesel engine can exceed safe limits and become sources of ignition. These surfaces need to be protected to avoid the danger of explosion.
Comments
Post a Comment